Overview
Hair loss, known as alopecia, can impact either the scalp or the entire body, and it may be temporary or permanent. Factors such as genetics, hormonal fluctuations, medical conditions, or natural aging can contribute to this condition. While hair loss can affect anyone, it’s more prevalent in men.
Baldness typically refers to significant hair loss from the scalp, often due to hereditary factors as one ages. Some individuals opt to embrace their hair loss without intervention, while others may use various methods such as hairstyles, cosmetics, hats, or scarves to conceal it. Alternatively, some choose from the available treatments to either prevent further hair loss or stimulate hair regrowth.
Before considering any hair loss treatment, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause of the condition and explore appropriate treatment options.
Book Consultation
Symptoms of Hair Loss
Hair loss can manifest in various ways, depending on its underlying cause, with symptoms appearing suddenly or gradually and affecting either the scalp or the entire body.
Common signs and symptoms of hair loss include:
1. Gradual thinning on the top of the head: This is the most typical type of hair loss, often seen as individuals age. In men, hair commonly recedes from the forehead’s hairline, while women may notice a widening of their hair part. An increasingly observed pattern of hair loss in older women is frontal fibrosing alopecia, characterized by a receding hairline.
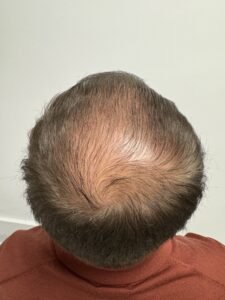
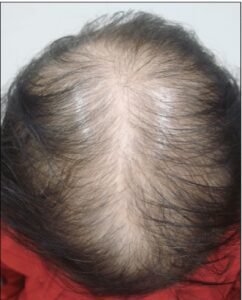
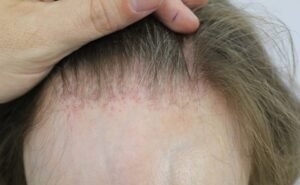
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
2. Circular or patchy bald spots: Some individuals experience hair loss in circular or patchy areas on the scalp, beard, or eyebrows. Prior to hair loss, the affected skin may become itchy or painful.

Alopecia Areata
3. Sudden loosening of hair: Physical or emotional shock can lead to hair becoming loose and shedding. Handfuls of hair may fall out during combing, washing, or even gentle tugging. This type of hair loss typically results in overall hair thinning and is usually temporary.
4. Full-body hair loss: Certain medical conditions or treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, can cause hair loss across the entire body. However, the hair often regrows after some time.
5. Scalp patches with scaling: Scalp scaling patches could indicate ringworm infection. Symptoms may include broken hair, redness, swelling, and sometimes oozing.
It’s essential to consult a doctor under the following circumstances:
- Persistent distress due to hair loss in yourself or your child warrants a doctor’s evaluation for potential treatment options.
- For women experiencing frontal fibrosing alopecia, early treatment consultation with a doctor is advisable to prevent significant permanent baldness.
- Sudden or patchy hair loss, or an unusual increase in hair shedding during grooming or washing, should prompt a consultation with a doctor, as it may signify an underlying medical condition requiring treatment.
Causes of hair loss
Hair loss can be attributed to several factors, with the most common causes including:
- Family History (Heredity): Hereditary conditions, such as androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness), are often responsible for hair loss as individuals age. This type of hair loss typically progresses gradually and follows predictable patterns, such as receding hairlines in men and thinning hair on the top partying in women.
- Hormonal Changes and Medical Conditions: Various hormonal changes and medical conditions can lead to both temporary and permanent hair loss. These may include hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid disorders. Medical conditions like alopecia areata, which is immune system-related and results in patchy hair loss, scalp infections such as ringworm, and trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, can also contribute to hair loss.
- Medications and Supplements: Certain medications, including those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, gout, and high blood pressure, may have hair loss as a side effect.
- Radiation Therapy: Hair loss can occur as a result of undergoing radiation therapy to the head, and regrowth may not necessarily occur in the same manner as before treatment.
- Stressful Events: Experiencing a significant physical or emotional shock can lead to a general thinning of hair several months later. However, this type of hair loss is usually temporary.
- Hairstyles and Treatments: Certain hairstyles that exert excessive tension on the hair, such as tight pigtails or cornrows, can cause traction alopecia, a type of hair loss. Additionally, hot-oil hair treatments and chemical processes like permanents may also contribute to hair loss. In cases where scarring occurs, hair loss could become permanent.
Traction Alopecia
Risk Factors of Hair Loss
Certain factors can increase the risk of experiencing hair loss, including:
- Family History: A family history of baldness on either the maternal or paternal side can predispose individuals to hair loss.
- Age: Hair loss becomes more common as individuals age, particularly with the onset of conditions like androgenic alopecia.
- Significant Weight Loss: Rapid or significant weight loss can sometimes trigger hair loss.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and lupus may contribute to hair loss.
- Stress: High levels of stress, whether physical or emotional, can be a risk factor for hair loss.
- Poor Nutrition: Inadequate nutrition, including deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, can impact hair health.
Prevention of Hair Loss
Prevention strategies for avoidable types of hair loss may include:
- Hair Care Practices: Treat your hair gently, using a detangler and avoiding excessive tugging, especially when wet. Consider using a wide-toothed comb to minimize hair breakage. Avoid harsh treatments like hot rollers, curling irons, hot-oil treatments, and permanents. Minimize tension on the hair from tight hairstyles that use rubber bands, barrettes, or braids.
- Medications and Supplements: Consult with your doctor about any medications or supplements you are taking that may contribute to hair loss.
- Sun Protection: Protect your hair from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light, as excessive exposure can damage the hair.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking may help reduce the risk of hair loss, as some studies suggest an association between smoking and baldness in men.
- Chemotherapy Cooling Cap: If undergoing chemotherapy, inquire about the possibility of using a cooling cap to reduce the risk of chemotherapy-induced hair loss.



